Demandez à un expert en fertilité : avantages de l’insémination artificielle
Chers lecteurs, au World Center of Baby, nous nous engageons à vous tenir informés de tout ce qui concerne la fertilité et les soins du bébé. C’est pourquoi nous avons posé à notre spécialiste de la reproduction Olga Sylaeva les questions les plus courantes et les plus passionnantes sur le traitement de la fertilité afin de vous expliquer clairement les choses complexes. Puisse ceci être votre guide ultime sur la grossesse, la naissance et la parentalité.
Quels sont les principaux avantages de l’insémination artificielle ?
L’insémination artificielle, comme toute autre intervention médicale, ne doit être pratiquée que pour des raisons médicales. Cela n’est pas fait parce que c’est à la mode ou parce que c’est prestigieux : les objectifs sociaux ne sont pas poursuivis ici. Cela se fait uniquement pour une condition médicale. Il y a un diagnostic, il y a un programme choisi et il y a sa mise en œuvre. Le principal avantage de l’insémination artificielle est qu’elle permet de concevoir et de donner naissance à un enfant à des personnes qui, malheureusement, ne sont pas médicalement en mesure de le faire naturellement.

Quels facteurs ont un impact sur le taux de réussite de l’insémination artificielle ?
Le principal critère par lequel nous évaluons le succès du programme est la naissance d’un bébé en bonne santé. Il existe des classifications internationales des critères de qualité des cliniques de fertilité. Nous rapportons et établissons nos propres statistiques sur les programmes qui réussissent et ceux qui ne le sont pas, comment améliorer les performances et ce qui affecte le résultat. Alors quels critères sont pris en compte ?
- l’âge du patient;
- nombre d’embryons transférés (un ou deux);
- caractéristiques des embryons transférés ;
- tests hormonaux avant le programme de FIV ;
- MIH (hormone inhibiteur de Müller, la plus informative) ;
- l’épaisseur de l’endomètre lors du transfert.
Tous ces critères reflètent une strate particulière de catégories de patients, et c’est dans ces catégories que les indicateurs de performance sont comparés. Ensuite, ils se sont synchronisés et forment une image du fonctionnement de la clinique de fertilité.

Quelle est la méthode d’insémination artificielle la plus courante ?
La méthode d’insémination artificielle principale et la plus courante est le programme de FIV. Que comprend-il ? La FIV s’accompagne souvent du programme ICSI (IntraCytoplasmic Sperm Injection). C’est lorsque chaque ovule est fécondé individuellement par un spermatozoïde particulièrement sélectionné. L’impact de ces programmes est plus important et, par conséquent, ils sont utilisés plus fréquemment.

Quels sont les autres types d’insémination artificielle ?
Il existe de nombreux types de fécondation in vitro. En option, il existe un programme de don d’ovules (lorsque, malheureusement, pour une raison quelconque, une femme n’est pas en mesure de donner ses ovules ou que leur qualité est impropre à la fécondation). Une autre option est la maternité de substitution (lorsqu’une femme ne peut pas porter un bébé naturellement pour des raisons médicales spécifiques). Des programmes de don de sperme sont également utilisés, et tous ces programmes peuvent être combinés dans n’importe quel ordre.
Il n’y a qu’une seule exception. Il est impossible de combiner le programme de maternité de substitution avec le don d’ovules et le don de sperme. Selon la législation ukrainienne, une mère porteuse ne peut pas donner d’ovules et l’un des parents d’intention doit avoir un lien biologique avec l’enfant qu’elle porte.

Que se passe-t-il pendant une IIU ?
IUI signifie Insémination Intra-utérine. C’est un programme peu utilisé car son taux de réussite ne dépasse malheureusement pas 15-20% (25% max). Il est généralement attribué aux couples qui n’ont encore rien essayé. On peut la prescrire quand on n’a pas déterminé le type d’infertilité (genèse dite ambiguë quand on ne peut pas la préciser). Pourtant, on sait que pendant plus d’un an, un couple ne parvient pas à concevoir naturellement. S’il n’y a pas encore deux ans d’infertilité, le programme peut être utilisé comme point de départ pour un traitement contre l’infertilité.
Quelle est la procédure d’insémination intra-utérine ?
L’homme donne du sperme pendant la période où la femme se prépare à l’ovulation. Nous traitons le sperme obtenu, ce qui signifie que nous le nettoyons et éliminons les fractions protéiques et tout le reste. Fondamentalement, nous faisons toutes les mêmes choses qu’une femme fait au niveau du col de l’utérus. Nous préparons les spermatozoïdes pour qu’ils pénètrent sans problème dans l’utérus, prêts à être fécondés.
Quels sont les risques de l’insémination artificielle ?
En fait, il existe certains risques. Le premier concerne la méthode d’obtention des œufs. Puisque les œufs ne quittent jamais le corps de la femme, ils se trouvent dans la cavité pelvienne de la femme. Ils s’y forment et y ovulent et, malheureusement, s’ils ne sont pas inséminés, ils y expirent. Donc, pour féconder des œufs dans un laboratoire, ils doivent d’une manière ou d’une autre entrer dans ce laboratoire. En conséquence, nous devons effectuer une ponction ovarienne, aspirer le liquide folliculaire, trouver les ovules, les laver et réaliser une insémination artificielle dans les conditions d’un laboratoire d’embryons. Certaines femmes peuvent être trop sensibles à la procédure. Ici, nous entrons sur les lieux et nous procédons à un examen médical approfondi de la femme.
D’autres complications peuvent être liées aux effets des médicaments eux-mêmes. Par exemple, les réactions allergiques : personne n’en est à l’abri. Même les vitamines peuvent provoquer des réactions allergiques. Il existe ensuite un syndrome d’hyperstimulation ovarienne, qui survient rarement mais peut néanmoins survenir. C’est lorsqu’une femme réagit par la croissance rapide d’un follicule, et même de petites doses de stimulants hormonaux peuvent déclencher ce syndrome. Mais il se soigne aussi à l’hôpital.

Comment une femme peut-elle se protéger de ces risques ?
Dans de tels cas, nous prescrivons des rendez-vous plus fréquents avec un médecin. Nous effectuons plus fréquemment des échographies ovariennes, surveillons le liquide libre dans le bassin bas et des analyses spécifiques de formule sanguine, déterminons l’état de la femme et réagissons en conséquence pour la sortir de la situation le plus efficacement possible.
Quelle quantité de sperme est nécessaire pour tomber enceinte ?
Habituellement, plus de 2 ml de sperme doivent contenir plus de 15 à 20 millions par millilitre de concentration de spermatozoïdes. Leur activité totale doit dépasser 50 %. Cependant, ce n’est pas seulement le nombre de spermatozoïdes par portion que l’on considère. Nous examinons également leur mobilité. C’est un autre critère par lequel nous l’évaluons. Et bien sûr, l’anatomie du spermatozoïde lui-même. Je veux dire, la morphologie : s’il a une tête propre, si sa pièce médiane est tordue et s’il a une ou deux queues. Ce sont ces facteurs qui affectent également la fertilité.

Combien de temps faut-il pour tomber enceinte grâce à l’insémination artificielle ?
Certaines patientes réussissent dès le premier essai, et un cycle menstruel sur lequel nous travaillons s’avère réussi. Cependant, certains couples essaient depuis des années, mais n’arrivent toujours pas à tomber enceinte. Chaque voyage est donc unique. Nous faisons tout notre possible pour réussir dès la première tentative.
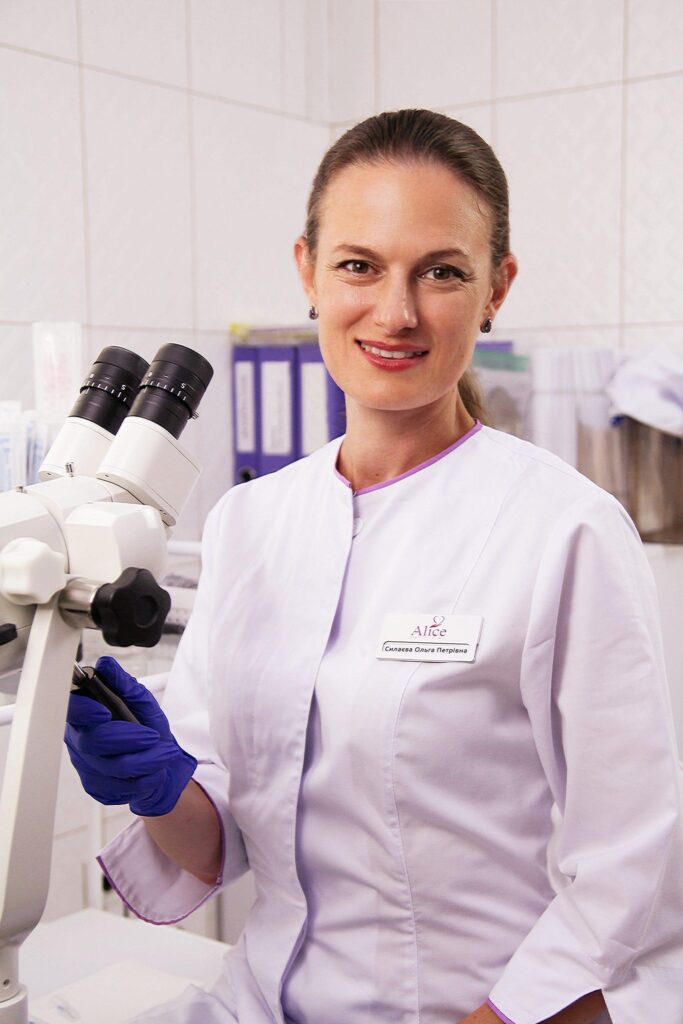
Olga Sylayeva MD
obstétricien-gynécologue en chef, thérapeute en reproduction
Le Dr Silayeva se spécialise dans les traitements de fertilité utilisant les technologies de procréation assistée, la FIV, le don d’ovules et les programmes de maternité de substitution. Grâce à elle, de nombreuses familles ont réalisé leur rêve et ont pu enfin accueillir leurs enfants.

Pregúntele al experto en fertilidad: ventajas de la inseminación artificial
Estimados lectores, en World Center of Baby tenemos el compromiso de mantenerlos informados sobre todo lo relacionado con la fertilidad y el cuidado del bebé. Es por eso que le preguntamos a nuestra especialista en reproducción Olga Sylaeva las preguntas más comunes y interesantes sobre el tratamiento de fertilidad para aclararle cosas complejas. Que esta sea su guía definitiva sobre embarazo, parto y paternidad.
¿Cuáles son las principales ventajas de la inseminación artificial?
La inseminación artificial, como cualquier otro procedimiento médico, debe realizarse únicamente por motivos médicos. No se hace porque esté de moda o porque sea prestigioso; aquí no se persiguen objetivos sociales. Se realiza únicamente por una condición médica. Hay un diagnóstico, hay un programa elegido y está su implementación. La principal ventaja de la inseminación artificial es que permite concebir y tener un hijo a aquellas personas que, lamentablemente, no pueden hacerlo de forma natural desde el punto de vista médico.

¿Qué factores afectan la tasa de éxito de la inseminación artificial?
El criterio principal por el cual evaluamos el éxito del programa es el nacimiento de un bebé sano. Existen clasificaciones internacionales de criterios de calidad de las clínicas de fertilidad. Informamos y elaboramos nuestras propias estadísticas sobre qué programas tienen éxito y cuáles no, cómo mejorar el rendimiento y qué afecta al resultado. Entonces ¿qué criterios se consideran?
- la edad del paciente;
- cantidad de embriones transferidos (uno o dos);
- características de los embriones que han sido transferidos;
- pruebas hormonales antes del programa de FIV;
- MIH (hormona inhibidora de Müller, la más informativa);
- el espesor del endometrio durante la transferencia.
Todos estos criterios reflejan un estrato particular de categorías de pacientes, y es en estas categorías donde se comparan los indicadores de desempeño. Luego se sincronizaron y se formaron una imagen de cómo funciona la clínica de fertilidad.

¿Cuál es el método más común de inseminación artificial?
El método principal y más común de inseminación artificial es el programa de FIV. ¿Qué incluye? La FIV suele ir acompañada del programa ICSI (inyección intracitoplasmática de espermatozoides). Es cuando cada óvulo es fecundado individualmente por un espermatozoide especialmente seleccionado. El impacto de estos programas es más significativo y, por tanto, se utilizan con mayor frecuencia.

¿Cuáles son los otros tipos de inseminación artificial?
Existen muchos tipos de fertilización in vitro. Como opción, existe un programa de donación de óvulos (cuando, lamentablemente, por alguna razón, la mujer no puede donar sus óvulos o su calidad no es apta para la fertilización). Otra opción es la gestación subrogada (cuando una mujer no puede tener un bebé de forma natural por motivos médicos específicos). También se utilizan programas de donación de esperma y todos estos programas pueden combinarse en cualquier orden.
Sólo hay una excepción. Es imposible combinar el programa de gestación subrogada con la donación de óvulos y la donación de esperma. Según la legislación ucraniana, una madre sustituta no puede ser donante de óvulos y uno de los padres de intención debe estar relacionado biológicamente con el niño que lleva la madre sustituta.

¿Qué sucede durante una IIU?
IUI significa Inseminación Intrauterina. Es un programa que se utiliza con poca frecuencia porque su tasa de éxito, lamentablemente, no supera el 15-20% (25% como máximo). Suele asignarse a parejas que aún no han probado nada. Podemos prescribirlo cuando no hemos determinado el tipo de infertilidad (la llamada génesis ambigua cuando no podemos especificarlo). Aún así, sabemos que desde hace más de un año, una pareja no puede concebir de forma natural. Si aún no han transcurrido dos años de infertilidad, el programa se puede utilizar como punto de partida para el tratamiento de la infertilidad.

¿Cuál es el procedimiento de inseminación intrauterina?
El hombre dona esperma durante el período en que la mujer se prepara para la ovulación. Procesamos el esperma obtenido, es decir, lo limpiamos y eliminamos las fracciones de proteínas y todo lo demás. Básicamente, hacemos las mismas cosas que hace una mujer en su cuello uterino. Preparamos los espermatozoides para que lleguen al útero sin problemas, listos para la fertilización.

¿Cuáles son los riesgos de la inseminación artificial?
De hecho, existen ciertos riesgos. El primero está relacionado con el método por el cual se obtienen los óvulos. Dado que los óvulos nunca abandonan el cuerpo de una mujer, se encuentran en la cavidad pélvica de la mujer. Se forman y ovulan allí y, lamentablemente, si no son inseminadas, expiran allí. Entonces, para fertilizar óvulos en un laboratorio, de alguna manera tienen que ingresar a ese laboratorio. En consecuencia, es necesario realizar una punción ovárica, aspirar líquido folicular, encontrar óvulos, lavarlos y realizar una inseminación artificial en las condiciones de un laboratorio de embriones. Algunas mujeres pueden ser demasiado sensibles al procedimiento. Aquí entramos en escena y le estamos haciendo un examen médico exhaustivo a la mujer.
Otras complicaciones pueden ser los efectos de los propios medicamentos. Por ejemplo, las reacciones alérgicas: nadie es inmune a ellas. Incluso las vitaminas pueden provocar reacciones alérgicas. Luego está el síndrome de hiperestimulación ovárica, que rara vez ocurre pero aún puede ocurrir. Es cuando la mujer responde con el rápido crecimiento de un folículo, e incluso pequeñas dosis de estimulantes hormonales pueden desencadenar este síndrome. Pero también se trata en el hospital.

¿Cómo puede una mujer protegerse de estos riesgos?
En tales casos, prescribimos citas más frecuentes con un médico. Realizamos ecografías de ovario con mayor frecuencia, monitorizamos el líquido libre en la zona baja de la pelvis y pruebas específicas de fórmula sanguínea, determinamos el estado de la mujer y reaccionamos en consecuencia para sacarla de la situación de la forma más eficaz posible.

¿Cuánto esperma se necesita para quedar embarazada?
Por lo general, más de 2 ml de esperma deben contener entre 15 y 20 millones por mililitro de concentración de espermatozoides. Su actividad total debe superar el 50%. Sin embargo, no sólo consideramos el número de espermatozoides por porción. También examinamos su movilidad. Este es otro criterio por el cual lo evaluamos. Y, por supuesto, la anatomía del propio espermatozoide. Me refiero a la morfología: si tiene una cabeza adecuada, si su pieza central está torcida y si tiene una o dos colas. Estos son los factores que también afectan la fertilidad.

¿Cuánto tiempo se tarda en quedar embarazada mediante inseminación artificial?
Algunas pacientes lo logran desde el primer intento y un ciclo menstrual con el que trabajamos resulta exitoso. Sin embargo, algunas parejas lo han intentado durante años, pero todavía no consiguen quedar embarazadas. Por eso cada viaje es único. Hacemos todo lo posible para tener éxito desde el primer intento.

Olga Sylayeva MD
obstetra-ginecólogo jefe, terapeuta reproductivo
La Dra. Silayeva se especializa en tratamientos de fertilidad utilizando tecnologías de reproducción asistida, FIV, donación de óvulos y programas de subrogación. Gracias a ella, muchas familias lograron su sueño y finalmente pudieron tener a sus hijos en brazos.

Fragen Sie einen Fruchtbarkeitsexperten: Vorteile der künstlichen Befruchtung
Liebe Leserinnen und Leser, wir vom World Center of Baby sind bestrebt, Sie über alles rund um Fruchtbarkeit und Babypflege auf dem Laufenden zu halten. Aus diesem Grund haben wir unserer Reproduktionsspezialistin Olga Sylaeva die häufigsten und spannendsten Fragen zur Kinderwunschbehandlung gestellt, um Ihnen komplexe Zusammenhänge zu verdeutlichen. Möge dies Ihr ultimativer Schwangerschafts-, Geburts- und Erziehungsratgeber sein.
Was sind die Hauptvorteile der künstlichen Befruchtung?
Eine künstliche Befruchtung darf wie jeder andere medizinische Eingriff nur aus medizinischen Gründen durchgeführt werden. Dies geschieht nicht, weil es in Mode ist oder weil es prestigeträchtig ist – soziale Ziele werden hier nicht verfolgt. Dies geschieht ausschließlich aus medizinischen Gründen. Es gibt eine Diagnose, es gibt ein ausgewähltes Programm und es gibt seine Umsetzung. Der Hauptvorteil der künstlichen Befruchtung besteht darin, dass sie es denjenigen ermöglicht, schwanger zu werden und ein Kind zur Welt zu bringen, die aus medizinischen Gründen leider nicht dazu in der Lage sind.

Welche Faktoren beeinflussen die Erfolgsquote der künstlichen Befruchtung?
Das Hauptkriterium, anhand dessen wir den Erfolg des Programms beurteilen, ist die Geburt eines gesunden Babys. Es gibt internationale Klassifikationen der Qualitätskriterien von Kinderwunschkliniken. Wir berichten und erstellen eigene Statistiken darüber, welche Programme erfolgreich sind und welche nicht, wie sich die Leistung verbessern lässt und was sich auf das Ergebnis auswirkt. Welche Kriterien werden also berücksichtigt?
- das Alter des Patienten;
- Anzahl der übertragenen Embryonen (ein oder zwei);
- Merkmale der übertragenen Embryonen;
- Hormontests vor dem IVF-Programm;
- MIH (Müllerian-hemmendes Hormon, das informativste);
- die Dicke des Endometriums während der Übertragung.
Alle diese Kriterien spiegeln eine bestimmte Schicht von Patientenkategorien wider, und in diesen Kategorien werden Leistungsindikatoren verglichen. Dann synchronisierten sie sich und machten sich ein Bild davon, wie die Fruchtbarkeitsklinik funktioniert.

Was ist die häufigste Methode der künstlichen Befruchtung?
Die wichtigste und häufigste Methode der künstlichen Befruchtung ist das IVF-Programm. Was beinhaltet es? IVF geht oft mit dem ICSI-Programm (Intrazytoplasmatische Spermieninjektion) einher. Dabei wird jede Eizelle einzeln durch ein speziell ausgewähltes Spermium befruchtet. Die Wirkung solcher Programme ist größer und sie werden daher häufiger eingesetzt.

Welche anderen Arten der künstlichen Befruchtung gibt es?
Es gibt viele Arten der In-vitro-Fertilisation. Als Option gibt es ein Eizellspendeprogramm (wenn eine Frau aus irgendeinem Grund leider nicht in der Lage ist, ihre Eizellen abzugeben oder deren Qualität für eine Befruchtung ungeeignet ist). Eine weitere Option ist die Leihmutterschaft (wenn eine Frau aus bestimmten medizinischen Gründen kein Kind auf natürlichem Weg zur Welt bringen kann). Es kommen auch Samenspendeprogramme zum Einsatz, wobei alle diese Programme in beliebiger Reihenfolge kombiniert werden können.
Es gibt nur eine Ausnahme. Es ist nicht möglich, das Leihmutterschaftsprogramm mit einer Eizellspende und einer Samenspende zu kombinieren. Gemäß der ukrainischen Gesetzgebung kann eine Leihmutter keine Eizellspenderin sein und einer der Wunscheltern muss mit dem Kind, das die Leihmutter austrägt, biologisch verwandt sein.

Was passiert während einer IUI?
IUI steht für Intrauterine Insemination. Es ist ein Programm, das selten verwendet wird, da seine Erfolgsquote leider nicht über 15-20 % (maximal 25 %) liegt. Es wird normalerweise Paaren zugewiesen, die noch nichts ausprobiert haben. Wir können es verschreiben, wenn wir die Art der Unfruchtbarkeit noch nicht bestimmt haben (die sogenannte mehrdeutige Art der Genese, wenn wir sie nicht genau bestimmen können). Dennoch wissen wir, dass ein Paar über ein Jahr lang nicht auf natürlichem Wege schwanger werden kann. Wenn die Unfruchtbarkeit seit zwei Jahren noch nicht besteht, kann das Programm als Ausgangspunkt für die Behandlung der Unfruchtbarkeit dienen.

Wie läuft die intrauterine Insemination ab?
Der Mann spendet Sperma während der Zeit, in der sich die Frau auf den Eisprung vorbereitet. Wir verarbeiten gewonnenes Sperma, das heißt, wir reinigen es und waschen die Proteinfraktionen und alles andere weg. Im Grunde machen wir die gleichen Dinge, die eine Frau an ihrem Gebärmutterhals macht. Wir bereiten die Spermien so vor, dass sie nahtlos in die Gebärmutter gelangen und dort zur Befruchtung bereit sind.

Was sind die Risiken einer künstlichen Befruchtung?
Tatsächlich bestehen gewisse Risiken. Die erste hängt mit der Methode zusammen, mit der Eier gewonnen werden. Da Eizellen den Körper einer Frau nie verlassen, befinden sie sich in der Beckenhöhle der Frau. Sie bilden sich dort und haben dort ihren Eisprung. Wenn sie nicht besamt werden, vergehen sie leider dort. Um Eizellen in einem Labor zu befruchten, müssen sie also irgendwie in dieses Labor gelangen. Dementsprechend müssen wir eine Eierstockpunktion durchführen, Follikelflüssigkeit absaugen, Eizellen finden, waschen und unter den Bedingungen eines Embryolabors eine künstliche Befruchtung durchführen. Einige Frauen reagieren möglicherweise zu empfindlich auf den Eingriff. Hier betreten wir den Tatort und führen eine gründliche medizinische Untersuchung der Frau durch.
Weitere Komplikationen können die Wirkung der Medikamente selbst sein. Zum Beispiel allergische Reaktionen – niemand ist davor gefeit. Auch Vitamine können allergische Reaktionen hervorrufen. Dann gibt es ein ovarielles Überstimulationssyndrom, das selten, aber dennoch auftreten kann. Dabei reagiert eine Frau mit einem schnellen Wachstum eines Follikels, und bereits geringe Dosen hormoneller Stimulanzien können dieses Syndrom auslösen. Es wird aber auch im Krankenhaus behandelt.

Wie kann sich eine Frau vor diesen Risiken schützen?
In solchen Fällen verschreiben wir häufigere Termine beim Arzt. Wir führen häufiger Ultraschalluntersuchungen der Eierstöcke durch, überwachen die freie Flüssigkeit im unteren Becken und spezifische Blutformeltests, ermitteln den Zustand der Frau und reagieren entsprechend, um sie so effizient wie möglich aus der Situation zu befreien.

Wie viel Sperma wird für eine Schwangerschaft benötigt?
Normalerweise müssen mehr als 2 ml Spermien eine Spermienkonzentration von über 15–20 Millionen pro Milliliter enthalten. Ihre Gesamtaktivität muss 50 % überschreiten. Wir berücksichtigen jedoch nicht nur die Anzahl der Spermien pro Portion. Wir untersuchen auch ihre Mobilität. Dies ist ein weiteres Kriterium, nach dem wir es bewerten. Und natürlich die Anatomie des Spermatozoons selbst. Ich meine, die Morphologie: ob es einen richtigen Kopf hat, ob sein Mittelstück gedreht ist und ob es einen oder zwei Schwänze hat. Dies sind die Faktoren, die auch die Fruchtbarkeit beeinflussen.

Wie lange dauert es, durch künstliche Befruchtung schwanger zu werden?
Manche Patientinnen schaffen es gleich beim ersten Versuch, und ein Menstruationszyklus, mit dem wir arbeiten, erweist sich als erfolgreich. Manche Paare versuchen es schon seit Jahren, können aber trotzdem nicht schwanger werden. Daher ist jede Reise einzigartig. Wir tun alles, um vom ersten Versuch an erfolgreich zu sein.

Olga Sylayeva MD
Chefarzt für Geburtshilfe und Gynäkologie, Reproduktionstherapeut
Dr. Silayeva ist auf Fruchtbarkeitsbehandlungen mit assistierten Reproduktionstechnologien, IVF, Eizellspende und Leihmutterschaftsprogrammen spezialisiert. Dank ihr konnten viele Familien ihren Traum verwirklichen und endlich ihre Kinder im Arm halten.

Ask Fertility Expert: Advantages of Artificial Insemination
Dear readers, at World Center of Baby, we are pledged to keep you informed on everything related to fertility and baby care. This is why we asked our reproductive specialist Olga Sylaeva the most common and exciting questions about fertility treatment to make complex things clear for you. May this be your ultimate pregnancy, birth and parenting guide.
What Are the Main Advantages of Artificial Insemination?
Artificial insemination, like any other medical procedure, must be performed only on medical grounds. It is not done because it is fashionable or because it is prestigious — social goals are not pursued here. It is done solely for a medical condition. There is a diagnosis, there is a chosen program, and there is its implementation. The main advantage of artificial insemination is that it makes it possible to conceive and give birth to a child to those who, unfortunately, are medically unable to do so naturally.

What Factors Impact the Success Rate of Artificial Insemination?
The main criterion by which we assess the program’s success is the birth of a healthy baby. There are international classifications of quality criteria of fertility clinics. We report and make our own statistics on what programs are successful and what are not, how to improve the performance, and what affects the result. So what criteria are considered?
- the age of the patient;
- amount of transferred embryos (one or two);
- characteristics of embryos that have been transferred;
- hormonal tests before the IVF program;
- MIH (Müllerian-inhibiting hormone, the most informative one);
- the thickness of the endometrium during transfer.
All of these criteria reflect a particular stratum of patient categories, and it is in these categories, performance indicators are compared. Then they synchronized, and they form a picture of how the fertility clinic works.

What Is the Most Common Method of Artificial Insemination?
The main and most common method of artificial insemination is the IVF program. What does it include? IVF often goes with the ICSI program (IntraCytoplasmic Sperm Injection). It’s when each egg is fertilized individually by a particularly selected spermatozoon selected. The impact of such programs is more significant, and, therefore, they are used more frequently.

What Are the Other Types of Artificial Insemination?
There are many types of in vitro fertilization. As an option, there is an egg donation program (when, unfortunately, for some reason, a woman is unable to give her eggs, or their quality unfits for fertilization). Another option is surrogacy (when a woman cannot bear a baby naturally for specific medical reasons). Sperm donation programs are also used, and all these programs may be combined in any order.
There is only one exception. It is impossible to combine the surrogacy program with egg donation and sperm donation. According to Ukrainian legislation, a surrogate mother cannot be an egg donor, and one of the intended parents must be biologically connected with the child the surrogate is carrying.

What Happens During an IUI?
IUI stands for Intrauterine Insemination. It’s a program that is infrequently used because its success rate, unfortunately, does not exceed 15-20% (25% max). It’s usually assigned to couples who haven’t tried anything yet. We can prescribe it when we haven’t determined the type of infertility (the so-called ambiguous kind of genesis when we can’t specify it). Still, we know that for over a year, a couple can’t conceive naturally. If it hasn’t been for two years of infertility yet, the program can be used as a starting point for infertility treatment.

What Is the Procedure of Intrauterine Insemination?
The man donates sperm during the period when the woman is preparing for ovulation. We’re processing obtained sperm, meaning we clear it and wash away the protein fractions and everything else. Basically, we do all the same things that a woman does in her cervix. We prepare sperm to get into the womb seamlessly, ready for fertilization.

What Are the Risks of Artificial Insemination?
In fact, there are certain risks. The first one is related to the method by which eggs are obtained. Since eggs never leave a woman’s body, they are in a woman’s pelvic cavity. They form in and ovulate there, and, unfortunately, if they’re not inseminated, they expire there. So in order to fertilize eggs in a laboratory, they have to somehow get into that lab. Accordingly, we must perform an ovarian puncture, aspirate follicular fluid, find eggs, wash them, and perform artificial insemination under the conditions of embryo-laboratory. Some women may be too sensitive to the procedure. Here, we enter the scene, and we’re doing a thorough medical examination of the woman.
Other complications may be the effects of the medications themselves. For instance, allergic reactions — no one is immune from them. Even vitamins can cause allergic reactions. Then there is an ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, which rarely but still may occur. It’s when a woman responds with the rapid growth of a follicle, and even small doses of hormonal stimulants can trigger this syndrome. But it’s also treated in hospital.

How Can a Woman Protect Herself From These Risks?
In such cases, we prescribe more frequent appointments with a doctor. We perform ovarian ultrasound tests more frequently, monitor free fluid in the low pelvis and specific blood-formula tests, and determine the woman’s condition and react accordingly to get her out of the situation as efficiently as possible.

How Much Sperm Is Required for Getting Pregnant?
Usually, more than 2 ml of sperm must contain over 15-20 million per milliliter of spermatozoa concentration. Their total activity must exceed 50%. However, it is not only the number of spermatozoa per portion that we consider. We also examine their mobility. This is another criterion by which we evaluate it. And, of course, the anatomy of the spermatozoon itself. I mean, the morphology: whether it has a proper head, whether its midpiece is twisted, and whether it has one or two tails. These are the factors that also affect fertility.

How Long Does It Take to Get Pregnant Through Artificial Insemination?
Some patients make it right from the first try, and one menstrual cycle we work with turns out to be successful. However, some couples have been trying for years, but they still can’t get pregnant. So every journey is unique. We do everything we can to succeed from the first attempt.

Olga Sylayeva M.D.
сhief obstetrician-gynecologist, reproductive therapist
Dr. Silayeva specializes in fertility treatments using assisted reproductive technologies, IVF, egg donation, and surrogфcy programs. Thanks to her, many families achieved their dream and were finally able to hold their children.

